Introduction
A Malonic Acid Manufacturing Plant Project Report is a detailed blueprint for establishing a facility that produces malonic acid, a versatile organic compound widely used in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and specialty chemicals. This report outlines the key steps, production processes, market outlook, financial considerations, and regulatory aspects associated with setting up a malonic acid manufacturing plant.
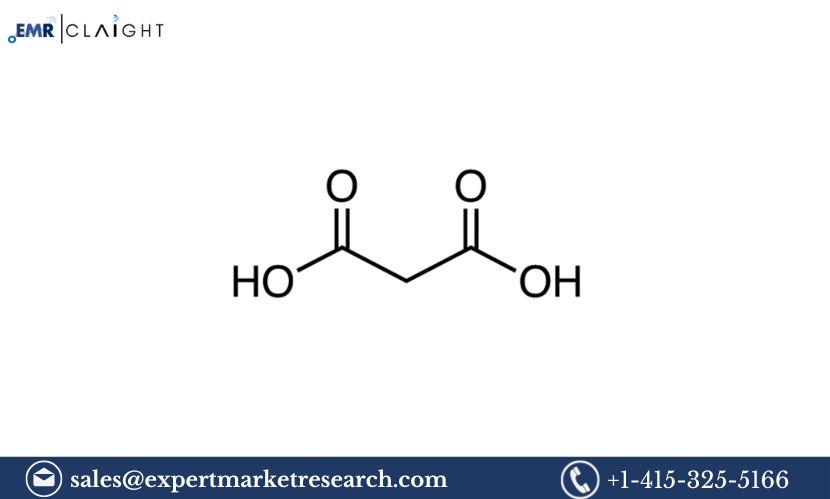
Malonic acid, with the chemical formula C3H4O4, is an important intermediate in organic chemistry. It is primarily used in the synthesis of other chemicals, including barbiturates, herbicides, and fragrances. The global demand for malonic acid has been on the rise, driven by its applications in various industries. This makes the establishment of a malonic acid manufacturing plant a potentially lucrative business opportunity for entrepreneurs and investors in the chemical manufacturing sector.
What is Malonic Acid?
Malonic acid, also known as propane-1,2,3-tricarboxylic acid, is a dicarboxylic acid with two carboxyl groups (-COOH) attached to a three-carbon chain. It is a key intermediate in organic synthesis due to its ability to undergo a variety of reactions, including esterification, decarboxylation, and amination.
Chemically, malonic acid is used as a building block for producing a wide range of derivatives and products, such as:
- Pharmaceuticals: In the production of barbiturates and other drugs.
- Agricultural Chemicals: As a precursor to herbicides and pesticides.
- Fragrances: Used in the synthesis of various perfumes.
- Polyesters and Resins: Used in the production of plastics and coatings.
Its versatility and wide range of applications make malonic acid an essential chemical in various industries.
Get a Free Sample Report with Table of Contents@
Market Overview of Malonic Acid
The market for malonic acid has been growing due to its increasing use in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other specialty chemicals. The demand for malonic acid is largely driven by the expansion of industries such as pharmaceuticals, agriculture, and manufacturing.
Key Drivers for Malonic Acid Demand:
-
Pharmaceutical Applications: Malonic acid is widely used in the production of barbiturates and other pharmaceutical intermediates. The rise in demand for these drugs, particularly in the treatment of epilepsy, anxiety, and other conditions, has increased the need for malonic acid.
-
Agricultural Demand: The growing need for efficient agricultural chemicals such as herbicides and pesticides, in order to meet the demands of modern agriculture, has fueled the demand for malonic acid.
-
Plastic and Resin Manufacturing: Malonic acid is used in the production of polyesters, resins, and plastics, particularly for coatings and advanced materials. As the demand for environmentally-friendly plastics and coatings grows, so does the demand for malonic acid.
-
Increasing Industrialization: With growing industrialization in emerging economies, the demand for specialty chemicals, including malonic acid, has expanded. The shift towards more chemical-based products, including in fragrances and agrochemicals, supports this trend.
The global market for malonic acid is expected to continue its growth trajectory, with regions like North America, Europe, and Asia-Pacific experiencing increasing demand for its diverse applications.
Production Process of Malonic Acid
The production of malonic acid typically involves the cyanohydrin synthesis method, which is one of the most commonly used industrial processes. The process involves a few critical steps, each requiring careful control to ensure the quality and yield of the product.
1. Cyanohydrin Synthesis
Malonic acid is primarily synthesized through the reaction of cyanoacetic acid with alkali in the presence of a catalyst. The reaction involves the following steps:
- Hydrolysis: The reaction between cyanoacetic acid and a base (usually sodium hydroxide) generates an intermediate compound known as a cyanohydrin.
- Decarboxylation: The intermediate compound undergoes decarboxylation, which removes a carbon dioxide molecule, leaving malonic acid.
2. Purification
After the synthesis, the resulting malonic acid is purified to remove any unreacted materials, solvents, and by-products. This is typically done using techniques such as:
- Filtration: To remove solid impurities.
- Crystallization: To obtain high-purity malonic acid crystals.
- Distillation: If necessary, to remove volatile impurities.
The final product must meet stringent quality control standards, as malonic acid is used in various critical applications, such as in pharmaceutical formulations.
3. Formulation and Packaging
Once purified, malonic acid is often formulated into various grades and packaged accordingly, depending on its end-use. It can be supplied as a powder, a crystalline solid, or in a liquid form, depending on the needs of the customer. Packaging must also comply with safety standards and ensure that the product is protected from contamination during transportation and storage.
Raw Materials for Malonic Acid Production
The production of malonic acid requires several key raw materials:
- Cyanoacetic Acid: The primary precursor in the cyanohydrin synthesis method.
- Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH): Used as a base in the hydrolysis reaction.
- Solvents: Organic solvents such as water, ethanol, and acetone may be used during various stages of the synthesis and purification process.
- Catalysts: Depending on the process, catalysts may be required to enhance the reaction efficiency.
Having reliable and cost-effective suppliers for these raw materials is crucial to maintaining consistent production and managing operational costs effectively.
Infrastructure and Equipment for the Manufacturing Plant
Setting up a malonic acid manufacturing plant requires specialized infrastructure and equipment to ensure the synthesis, purification, and packaging processes run smoothly. Key equipment and infrastructure include:
-
Reaction Vessels: These are required for carrying out the cyanohydrin synthesis, which typically happens in large reactors under controlled conditions of temperature and pressure.
-
Purification Units: Filtration units, crystallizers, and distillation columns are essential to purify the final product and ensure it meets required quality standards.
-
Storage Tanks: For the intermediate compounds and finished product, appropriate storage tanks must be installed to ensure that malonic acid is stored safely and securely.
-
Quality Control Labs: A dedicated laboratory is essential for conducting tests on the malonic acid to ensure that the product meets the necessary purity and quality specifications. This includes checking for contaminants, particle size distribution, and chemical composition.
-
Packaging Lines: Automated packaging lines ensure that the malonic acid is packaged efficiently, whether it is in bulk for industrial use or in smaller quantities for specialty applications.
-
Environmental Control Systems: Given the nature of chemical manufacturing, proper waste management and environmental control systems are essential to meet regulatory requirements and minimize environmental impact.
Financial Considerations and Investment
Setting up a malonic acid manufacturing plant involves substantial capital investment, with significant costs related to land acquisition, plant construction, equipment purchase, raw material procurement, and labor. The primary financial considerations include:
- Capital Investment: Costs associated with land, construction, and installation of production and purification equipment.
- Raw Material Costs: Procurement of cyanoacetic acid, sodium hydroxide, and other necessary chemicals and solvents.
- Labor Costs: Skilled labor is required for plant operations, including chemical engineers, plant operators, and quality control personnel.
- Operating Costs: These include utilities (electricity, water), maintenance costs, and raw material consumption.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring the plant complies with all local and international regulations may involve costs for certification, audits, and safety measures.
A detailed financial plan, including projected cash flows, profit margins, and break-even analysis, is essential to determine the plant's economic viability.
Regulatory and Safety Compliance
The malonic acid manufacturing process involves chemicals that can be hazardous. Therefore, compliance with various regulations and ensuring a safe working environment are crucial to the plant’s operation. Key regulatory and safety considerations include:
- Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP): Ensuring that the facility meets GMP standards is essential for producing high-quality chemicals and maintaining product integrity.
- Environmental Regulations: The plant must comply with environmental laws regarding waste management, emissions, and water usage. Efforts must be made to minimize the plant's environmental footprint.
- Health and Safety Standards: Occupational safety protocols, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and proper ventilation systems, must be in place to protect workers from exposure to hazardous chemicals.
Market Research and Feasibility Study
Before establishing a malonic acid manufacturing plant, it is essential to conduct a thorough market research and feasibility study. The study should cover:
- Demand Forecasting: Analyzing the current and future demand for malonic acid in various industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and plastics.
- Supply Chain Analysis: Identifying reliable suppliers for raw materials and establishing an efficient logistics system.
- Competitive Analysis: Understanding the competitive landscape and pricing strategies of existing malonic acid manufacturers.
- Financial Feasibility: Assessing the required capital, operating costs, revenue projections, and return on investment (ROI) to determine the profitability of the plant.
FAQ
1. What is malonic acid used for?
Malonic acid is used in a variety of industries, including pharmaceuticals (for barbiturate synthesis), agrochemicals (for herbicides), and the production of polyesters and resins.
2. What are the raw materials required for malonic acid production?
Key raw materials include cyanoacetic acid, sodium hydroxide, organic solvents, and catalysts.
3. What is the production process for malonic acid?
Malonic acid is produced using the cyanohydrin synthesis method, involving the reaction of cyanoacetic acid with a base, followed by hydrolysis, decarboxylation, and purification.
4. What is the market demand for malonic acid?
The demand for malonic acid is driven by its applications in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and industrial chemicals. The growing need for specialty chemicals in these sectors contributes to its market growth.
5. What are the main challenges in setting up a malonic acid manufacturing plant?
Challenges include securing a stable supply of raw materials, ensuring regulatory compliance, maintaining quality control, and managing high capital investment and operational costs.
Related Reports
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-personal-loan-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-plastic-packaging-market
https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au/reports/australia-recruitment-market
Media Contact:
Company Name: Claight Corporation
Contact Person: Lewis Fernandas, Corporate Sales Specialist — U.S.A.
Email: sales@expertmarketresearch.com
Toll Free Number: +1–415–325–5166 | +44–702–402–5790
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA
Website: www.expertmarketresearch.com
Aus Site: https://www.expertmarketresearch.com.au